Comparison Direct/Indirect
|
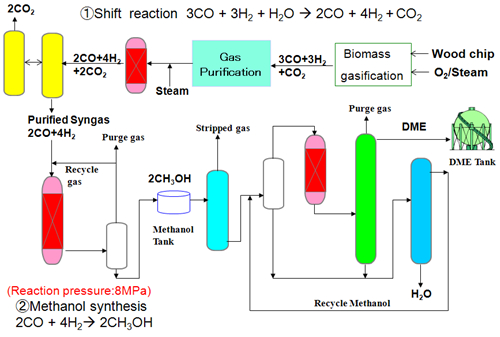
Comparison between Indirect method and Direct method for DME production process flow from woody biomass DME production process flow from woody biomass is shown in Figure 4-A for Indirect method and in Figure 4-B for Direct method. In comparison with the Indirect method, process configuration of the Direct method is simpler, number of equipment is smaller, synthesis pressure is lower, consequently lower plant cost and operation cost is expected. Carbon coming from raw material of woody biomass goes out of the process as product DME and CO2. As cold gas efficiency (heating value of product DME/heating value of raw material) of the Direct method is higher than that of the Indirect method, CO2 emission from the Direct method is expected lower. Indirect method process flow (Figure 4-A) H2/CO ratio of synthesis gas obtained by woody biomass gasification is near 1. As this ratio is lower than that required for methanol synthesis reaction, after gas purification, it is adjusted to 2 by water gas shift reaction (H2O+CO → H2+CO2) and CO2 is removed. Adjusted synthesis gas is pressurized to 8MPa and converted into methanol in methanol synthesis reactor. Produced methanol and un-reacted synthesis gas are cooled and separated into liquid methanol and un-reacted gas. Unreacted gas is recycled and liquid methanol is stored in intermediate tank. After dissolved gas in liquid methanol is separated in stripper, liquid methanol is heated for vaporization. Methanol gas enters into dehydration reactor to be converted into DME. DME, by-produced water and unreacted methanol are separated by two distillation columns. Un-reacted methanol is recycled. Product DME is liquefied by cooling and stored in DME tank. As by-produced water contains residual methanol, waste water treatment is necessary.
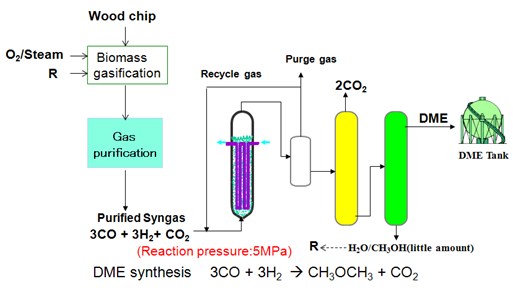
Direct method process flow (Figure 4-B) As H2/CO ratio of synthesis gas is near 1, the synthesis gas is pressurized to 5MPa after gas purification and introduced into the slurry phase DME synthesis reactor to be converted into DME. Produced DME is liquefied by cooling with methanol and water a little by-produced and separated from un-reacted gas. By-produced CO2 is absorbed in liquid DME. Unreacted synthesis gas is recycled into the DME synthesis reactor. CO2 in DME is separated in CO2 separation column. DME is purified in the following DME purification column. Selectivity of methanol and water in the DME synthesis reactor is very low and mixture of methanol and water coming out of the DME purification column bottom is of little amount. This mixture is recycled into the biomass gasification unit and then waste water treatment is unnecessary. Product DME is liquefied by cooling and stored in DME tank.
|
| « prev | top | next » |
 Japanese
Japanese English |
English |